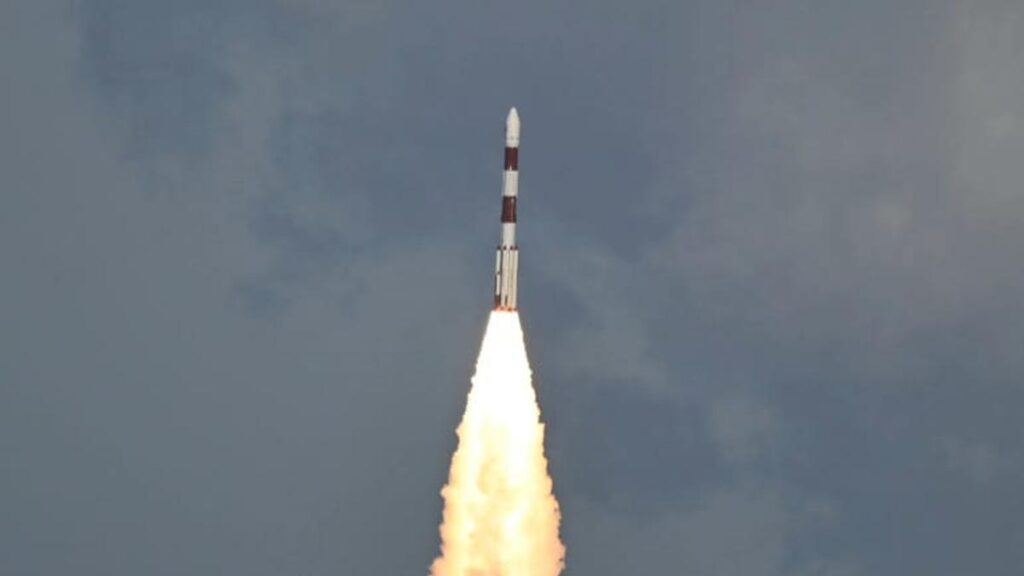
Sriharikota, December 5, 2024 – In another monumental achievement for Indian space exploration, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully launched the PSLV-C59 rocket carrying the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Proba-3 satellites from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, on Thursday. The mission, initially scheduled for December 4, was rescheduled to December 5 due to a last-minute anomaly in the propulsion system.
“Mission Success! The PSLV-C59/Proba-3 Mission has successfully achieved its launch objectives, deploying ESA’s satellites into their designated orbit with precision,” ISRO announced on X.
PSLV-C59 – A Mission Redefining Space Collaboration
A Mission Redefining Space Collaboration
The PSLV-C59 mission underscores India’s growing role as a global leader in space technology. The Proba-3 satellites (Project for Onboard Anatomy) are ESA’s innovative contribution to solar research. These two spacecraft are designed to fly in close formation, maintaining precision up to a millimeter, to study the Sun’s corona—the outermost part of the Sun’s atmosphere.
ISRO, in collaboration with its commercial arm NewSpace India Limited (NSIL), executed the launch with precision, earning accolades from ESA and global stakeholders. This success builds upon ISRO’s legacy of collaboration with ESA, starting with the launch of Proba-1 in 2001.
Rescheduled Launch and Anomaly Resolution
Originally set for December 4, the launch was postponed just minutes before liftoff due to an anomaly detected in the propulsion system of one of the satellites. Demonstrating technical rigor and problem-solving expertise, ISRO addressed the issue swiftly, rescheduling the mission for 4:04 PM on December 5. A revised countdown followed, culminating in a flawless launch.
The agency emphasized the importance of safety and mission assurance. “The anomaly was identified, resolved, and validated through comprehensive checks, ensuring the mission’s success,” said ISRO Chairman S. Somanath.
Proba-3: A Technological Marvel
The Proba-3 mission represents a leap in space research and innovation. It comprises two spacecraft, Coronagraph and Occulter, designed to operate in tandem. These satellites will fly in a stacked configuration before separating to perform coordinated maneuvers in orbit.
The mission’s primary goal is to demonstrate precise formation flying, a capability critical for advanced space missions. By creating an artificial solar eclipse in space, the satellites will study the Sun’s corona, shedding light on phenomena such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections, which have significant implications for space weather forecasting.
ISRO’s Role in Global Space Missions
The PSLV-C59 mission reaffirms ISRO’s reputation as a reliable partner for international space agencies. Over the years, India’s PSLV (Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle) program has been pivotal in launching satellites for various global clients, showcasing technical excellence and cost-effectiveness.
ISRO’s collaboration with ESA on Proba-3 highlights the strategic alignment of scientific goals between the two agencies. ESA Director Josef Aschbacher lauded the partnership, stating, “ISRO’s technical expertise and dedication to mission success have made this launch a significant milestone for ESA’s solar research program.”
A Growing Commercial Space Industry
The mission also underscores the rise of NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) as a key player in the global space market. As ISRO’s commercial arm, NSIL played a crucial role in securing the contract for the Proba-3 launch. This success is expected to bolster India’s position in the lucrative commercial satellite launch market.
International Recognition and Future Prospects
Global leaders in space exploration have congratulated ISRO on its achievement. “India has once again demonstrated its leadership in space technology. The successful launch of Proba-3 reflects the power of international collaboration in advancing scientific research,” said NASA Administrator Bill Nelson.
The mission also sets the stage for future collaborative projects between ISRO and ESA. “We are excited to continue working with ISRO on innovative missions that push the boundaries of space science,” said ESA’s Proba-3 mission head, Klaus Steiger.
Key Highlights of PSLV-C59/Proba-3 Mission
- Rocket: PSLV-C59 (Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle)
- Launch Date: December 5, 2024, 4:04 PM IST
- Launch Site: Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh
- Payload: Two Proba-3 satellites (Coronagraph and Occulter)
- Objective: Precise formation flying and study of the Sun’s corona
- Orbit: Designated low Earth orbit with millimeter-level precision
Celebrating India’s Space Prowess
The successful launch of PSLV-C59 is a testament to ISRO’s unwavering commitment to pushing the boundaries of space exploration. It not only advances solar research but also reinforces India’s position as a leading spacefaring nation. With this milestone, ISRO continues to inspire the global scientific community, paving the way for more ambitious missions.
As the Proba-3 satellites commence their mission, the world looks forward to groundbreaking insights into solar activity, which could transform our understanding of the Sun and its impact on Earth.